God Shiva, photographs of Lord Shiva and the 12 Jyotirlinga how to reach there.
Shiva
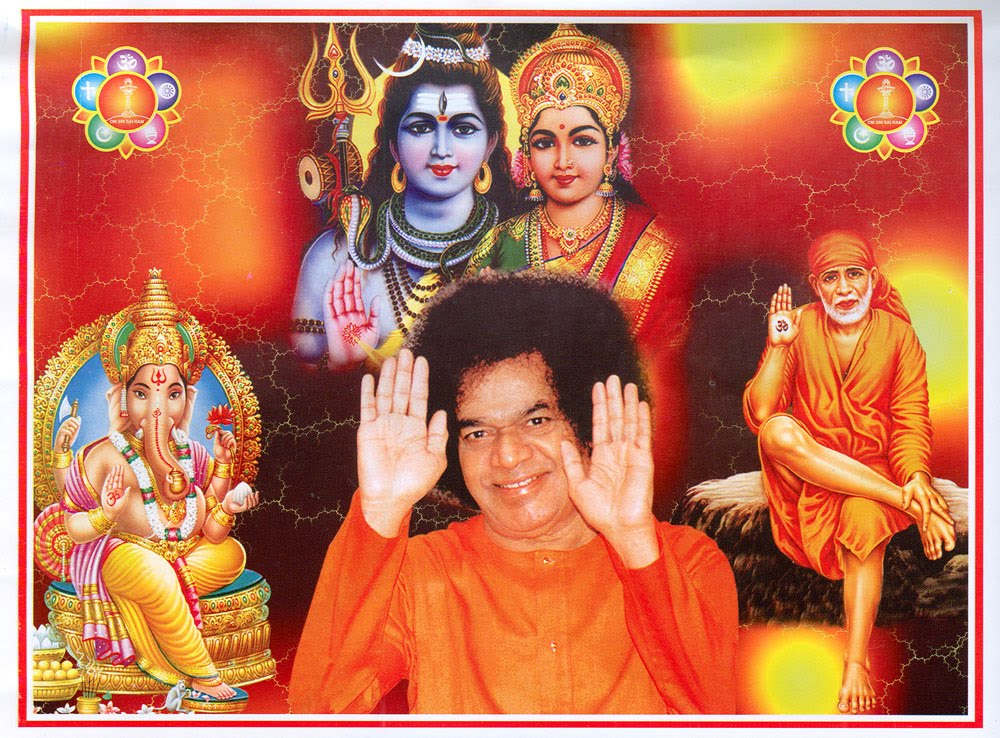
Shiva (lit. "Auspicious one") is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. Within Shaivism he is viewed as the Supreme deity, whereas in other branches of Hinduism such as the Smarta tradition he is worshipped as one of the six manifestations of the Divine. Followers of Hinduism who focus their worship upon Shiva are called Shaivites or Shaivas (Sanskrit Śaiva). His role as the primary deity of Shaivism is reflected in his epithets Mahādeva ("great god"; mahā = great + deva = god),Maheśhvara ("great lord"; mahā = great + īśhvara = lord), and Parameśhvara ("Supreme Lord"). Shaivism, along with Vaiṣṇava traditions that focus on Vishnu, and Śākta traditions that focus on the goddess (Devī) are three of the most influential denominations in Hinduism.
Shiva is one of the six primary forms of the Divine in Smartism, a denomination of Hinduism that puts particular emphasis on six deities, the other five being Vishnu, Shakti, Ganesha, Kartikkeya and Surya. In some other Hindu denominations, Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva represent the three primary aspects of the divine in Hinduism and are collectively known as the Trimurti. In this school of religious thought, Brahma is the creator, Vishnu is the maintainer or preserver, and Shiva is the destroyer or transformer.
Shiva is usually worshipped as the Shiva linga. In images, he is generally represented as immersed in deep meditation or dancing the Tandava upon the demon of ignorance in his manifestation of Nataraja, the lord of the dance.
Etymology
The Sanskrit word Shiva is an adjective meaning kind, friendly, gracious, or auspicious. As a proper name it means "The Auspicious One", used as a euphemistic name for Rudra. In simple English transliteration it is written either as Shiva or Siva. Pronunciation is written in the International Phonetic Alphabet as IPA: [ɕivə]. The adjective śiva meaning "auspicious" is used as an attributive epithet not particularly of Rudra, but of several other Vedic deities. In the Rig Veda, Indra uses this word to describe himself several times. (2:20:3, 6:45:17, 8:93:3)
In Tamil, Shiva literally means "the supreme one". Adi Sankara in his interpretation of the name Shiva, the 27th and 600th name of Vishnu sahasranama interprets Shiva to mean either "The Pure One", the One who is not affected by three Gunas of Prakrti, Sattva, Rajas and Tamas or "the One who purifies everyone by the very utterance of His name." [15] Swami Chinmayananda, in his translation of Vishnu sahasranama further elaborates on that verse: Shiva means the One who is eternally pure, or the One who can never have any contamination of the imperfection of Rajas and Tamas.
The Sanskrit word śaiva means "relating to the god Shiva", and this term is the Sanskrit name both for one of the principal sects of Hinduism, and for a member of one of those sects. It is used as an adjective to characterize certain beliefs and practices, such as Shaivism.
The name Shiva, in one interpretation, is also said to have derived from the Dravidian word "Siva" meaning "to be red". It is the equivalent of Rudra, "the red" RigVeda.
Historical Development
The worship of Shiva is a pan-Hindu tradition, practiced widely across all of India, Nepal and Sri Lanka. Modern historians believe that the figure of Shiva as we know him today was built-up over time, with the ideas of many regional sects being amalgamated into a single figure. How the persona of Shiva converged as a composite deity is not well-documented. Axel Michaels explains the composite nature of Shaivism as follows:
Like Vişņu, Śiva is also a high god, who gives his name to a collection of theistic trends and sects: Śaivism. Like Vaişņavism, the term also implies a unity which cannot be clearly found either in religious practice or in philosophical and esoteric doctrine. Furthermore, practice and doctrine must be kept separate.
An example of assimilation took place in Maharashtra, where a regional deity named Khandoba is a patron deity of farming and herding castes. The foremost center of worship of Khandoba in Maharashtra is in Jejuri. Khandoba has been assimilated both as a name for Karttikya and also as a form of Shiva himself in which case he is worshipped in the form of a lingam. Khandoba's varied associations also include an indentification with Surya. The derivation of the name Khandoba has been variously interpreted, and M. S. Mate says that the most commonly-held belief is that it was a distorted form of Skanda, but also notes alternate theories.
The Pashupati Seal
A seal discovered during the excavation of Mohenjo-daro has drawn attention as a possible representation of a "proto-Shiva" figure. This "Pashupati" (Lord of Animals,or Lord of Beings Sanskrit paśupati) seal shows a seated figure, possibly ithyphallic, surrounded by animals. Sir John Marshall and others have claimed that this figure is a prototype of Shiva, and have described the figure as having three faces, seated in a "yoga posture" with the knees out and feet joined. However, this claim is not without its share of critics with some modern academics like Gavin Flood and John Keay characterizing them as unfounded.
Rudra
Shiva as we know him today shares many features with the Vedic god Rudra and both Shiva and Rudra are viewed as the same personality in a number of Hindu traditions. Rudra, the god of the roaring storm, is usually portrayed in accordance with the element he represents as a fierce, destructive deity.
The oldest surviving text of Hinduism is the Rig Veda, which is dated to between 1700-1100 BCE based on linguistic and philological evidence. A god named Rudra is mentioned in the Rig Veda. The name Rudra is still used as a name for Shiva. In RV 2.33 he is described as the "Father of the Maruts", a group of storm gods. Furthermore, the Rudram, one of the most sacred hymns of Hinduism found both in the Rig and the Yajur Vedas, and addressed to Rudra, invokes him as Shiva in several instances.
The identification of Shiva with the older god Rudra is not universally accepted, as Axel Michaels explains:
To what extent Śiva's origins are in fact to be sought in Rudra is extremely unclear. The tendency to consider Śiva an ancient god is based on this identification, even though the facts that justify such a far-reaching assumption are meager.
Rudra is called "The Archer" (Sanskrit: Śarva) and the arrow is an essential attribute of Rudra. This name appears in the Shiva Sahasranama, and R. K. Sharma notes that it is used as a name of Shiva often in later languages. The word is derived from the Sanskrit root śarv- which means "to injure" or "to kill" and Sharma uses that general sense in his interpretive translation of the name Śarva as "One who can kill the forces of darkness". The names Dhanvin ("Bowman") and Bāṇahasta ("Archer", literally "Armed with arrows in his hands") also refer to archery.
Identification with Vedic Deities
Shiva's rise to a major position in the pantheon was facilitated by his identification with a host of Vedic deities, including Agni, Indra, Prajāpati, Vāyu, and others.
Agni
Rudra and Agni have a close relationship. The identification between Agni and Rudra in the Vedic literature was an important factor in the process of Rudra's gradual development into the later character as Rudra-Shiva. The identification of Agni with Rudra is explicitly noted in the Nirukta, an important early text on etymology, which says "Agni is called Rudra also". The interconnections between the two deities are complex, and according to Stella Kramrisch:
The fire myth of Rudra-Śiva plays on the whole gamut of fire, valuing all its potentialities and phases, from conflagration to illumination.
In the Śatarudrīa, some epithets of Rudra such as Sasipañjara ("Of golden red hue as of flame") and Tivaṣīmati ("Flaming bright") suggest a fusing of the two deities. Agni is said to be a bull and Lord Shiva possesses a bull as his vehicle, Nandi. The horns of Agni, who is sometimes characterized as a bull, are mentioned. In medieval sculpture both Agni and the form of Shiva known as Bhairava have flaming hair as a special feature.
Indra
Koenraad Elst proposes that Shiva of Puranic Hinduism is a continuation of the Vedic Indra. He gives several reasons for his hypothesis. Both Shiva and Indra are known for having a thirst for Soma. Both are associated with mountains, rivers, male fertility, fierceness, fearlessness, warfare, transgression of established mores, the Aum sound, the Supreme Self. In the Rig Veda the term śiva is used to refer to Indra.
Indra, like Shiva, is likened to a bull. In the Rig Veda, Rudra is the father of the Maruts, but he is never associated with their warlike exploits as is Indra. In the present form of Hinduism, Indra and Shiva are considered as distinct deities.
Attributes
According to Gavin Flood, "Śiva is a god of ambiguity and paradox", whose attributes include opposing themes. The ambivalent nature of this deity is apparent in some of his names and the stories told about him.
Destroyer versus Benefactor
In the Yajurveda two contrary sets of attributes for both malignant or terrific and benign or auspicious forms can be found, leading Chakravarti to conclude that "all the basic elements which created the complex Rudra-Śiva sect of later ages are to be found here." In the Mahabharata, Shiva is depicted as "the standard of invincibility, might, and terror", as well as a figure of honor, delight, and brilliance. The duality of Shiva's fearful and auspicious attributes appears in contrasted names.
The name Rudra reflects his fearsome aspects. According to traditional etymologies, the Sanskrit name Rudra is derived from the root rud- which means "to cry, howl." Stella Kramrisch notes a different etymology connected with the adjectival form raudra, which means wild, of rudra nature, and translates the name Rudra as "the Wild One" or "the Fierce God". R. K. Sharma follows this alternate etymology and translates the name as "Terrible". Hara is an important name that occurs three times in the Anushasanaparvan version of the Shiva sahasranama, where it is translated in different ways each time it occurs, following a commentorial tradition of not repeating an interpretation. Sharma translates the three as "One who captivates", "One who consolidates", and "One who destroys." Kramrisch translates it as "The Ravisher". Another of Shiva's fearsome forms is as Kāla, "Time", and as Mahākāla, "Great Time", which ultimately destroys all things. Bhairava, "Terrible" or "Frightful" is a fierce form associated with annihilation.
In contrast, the name Śaṇkara, "Beneficent" or "Conferring Happiness" reflects his benign form. This name was adopted by the great Vedanta philosopher Śaṇkara (c. 788-820 CE), who is also known as Shankaracharya. The name Śambhu, "Causing Happiness", also reflects this benign aspect.
Ascetic versus Householder
He is depicted as both an ascetic yogin and as a householder, roles which are mutually exclusive in Hindu society. When depicted as a yogin he may be shown sitting and meditating. His epithet Mahāyogin (The Great Yogi: Mahā = great, Yogin = one who practices Yoga) refers to his association with yoga. While Vedic religion was conceived mainly in terms of sacrifice, it was during the Epic period that concepts of tapas, yoga, and asceticism, became more important, and the depiction of Shiva as an ascetic sitting in philosophical isolation reflects these later concepts.
As a family man and householder he has a wife, Parvati (also known as Umā), and two sons, Ganesha and Skanda. His epithet Umāpati ("The husband of Umā") refers to this idea, and Sharma notes that two other variants of this name that mean the same thing, Umākānta and Umādhava, also appear in the sahasranama. Umā in epic literature is known by many names, including Pārvatī. She is identified with Devi, the Divine Mother, and with Shakti (divine energy).
Shiva and Parvati are the parents of Karthikeya and Ganesha. Karthikeya is worshipped in southern India (especially in Tamil Nadu and Karnataka) by the names Subrahmanyan, Shanmughan, Swaminathan and Murugan, and in northern India, is better known by the names Skanda, Kumara, or Karttikeya.
Nataraja
The depiction of Shiva as Nataraja ("Lord of Dance") is popular. The names Nartaka ("Dancer") and Nityanarta ("Eternal Dancer") appear in the Shiva Sahasranama. His association with dance and also with music is prominent in the Puranic period. In addition to the specific iconographic form known as Nataraja, various other types of dancing forms are found in all parts of India, with many well-defined varieties in Tamil Nadu (in southern India) in particular.
Dakṣiṇāmūrti
Dakṣiṇāmūrti literally describes a form (mūrti) of Shiva facing south (dakṣiṇa). This form represents Shiva in his aspect as a teacher of yoga, music, and wisdom, and giving exposition on the shastras. This iconographic form for depicting Shiva in Indian art is mostly from Tamil Nadu. Elements of this motif can include Shiva seated upon a deer-throne and surrounded by sages who are receiving his instruction.
Mruthyunjaya
Literally translated as 'victor over death', this is an aspect of Shiva worshipped as the conqueror of Death as manifested in the Hindu lord of death, Yama. The particular legend in question deals with the sage Markandeya, who was fated to die at the age of sixteen. On account of the sage's worship and devotion to Shiva, the Lord vanquished Yama to liberate his devotee from death. Shiva is often worshipped as Mruthyunjaya by the aged or ill, to ward off death and mitigate its harshness when it does occur. He is worshipped as such at the temples of Thirupainyeeli, near Trichinopoly, and at a shrine in Thirukadaiyur, near Chidambaram.
Ardhanarishvara
An iconographic representation of Shiva called Ardhanarishvara shows him with one half of the body as male, and the other half as female. According to Ellen Goldberg, the traditional Sanskrit name for this form, (Ardhanārīśvara) is best translated as "the lord who is half woman", and not as "half-man, half-woman".
Tripurāntaka
Shiva is often depicted as an archer in the act of destroying the triple fortresses, Tripura, of the Asuras. Shiva's name Tripurāntaka, "Ender of Tripura", refers to this important story.
Lingam
Apart from anthropomorphic images of Shiva, the worship of Shiva in the form of a lingam is also important. These are depicted in various forms. One common form is the shape of a vertical rounded column.
The Five Mantras
Five is a sacred number for Shiva. One of his most important mantras has five syllables (namaḥ śivāya).
Shiva's body is said to consist of five mantras, called the pañcabrahmans: As forms of god, each of these have their own names and distinct iconography:
Through these transcendent categories, Śiva, the ultimate reality, becomes the efficient and material cause of all that exists.
According to the Pañcabrahma Upanishad:
One should know all things of the phenomenal world as of a fivefold character, for the reason that the eternal verity of Śiva is of the character of the fivefold Brahman.
Shiva is one of the six primary forms of the Divine in Smartism, a denomination of Hinduism that puts particular emphasis on six deities, the other five being Vishnu, Shakti, Ganesha, Kartikkeya and Surya. In some other Hindu denominations, Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva represent the three primary aspects of the divine in Hinduism and are collectively known as the Trimurti. In this school of religious thought, Brahma is the creator, Vishnu is the maintainer or preserver, and Shiva is the destroyer or transformer.
Shiva is usually worshipped as the Shiva linga. In images, he is generally represented as immersed in deep meditation or dancing the Tandava upon the demon of ignorance in his manifestation of Nataraja, the lord of the dance.
Etymology
The Sanskrit word Shiva is an adjective meaning kind, friendly, gracious, or auspicious. As a proper name it means "The Auspicious One", used as a euphemistic name for Rudra. In simple English transliteration it is written either as Shiva or Siva. Pronunciation is written in the International Phonetic Alphabet as IPA: [ɕivə]. The adjective śiva meaning "auspicious" is used as an attributive epithet not particularly of Rudra, but of several other Vedic deities. In the Rig Veda, Indra uses this word to describe himself several times. (2:20:3, 6:45:17, 8:93:3)
In Tamil, Shiva literally means "the supreme one". Adi Sankara in his interpretation of the name Shiva, the 27th and 600th name of Vishnu sahasranama interprets Shiva to mean either "The Pure One", the One who is not affected by three Gunas of Prakrti, Sattva, Rajas and Tamas or "the One who purifies everyone by the very utterance of His name." [15] Swami Chinmayananda, in his translation of Vishnu sahasranama further elaborates on that verse: Shiva means the One who is eternally pure, or the One who can never have any contamination of the imperfection of Rajas and Tamas.
The Sanskrit word śaiva means "relating to the god Shiva", and this term is the Sanskrit name both for one of the principal sects of Hinduism, and for a member of one of those sects. It is used as an adjective to characterize certain beliefs and practices, such as Shaivism.
The name Shiva, in one interpretation, is also said to have derived from the Dravidian word "Siva" meaning "to be red". It is the equivalent of Rudra, "the red" RigVeda.
Historical Development
The worship of Shiva is a pan-Hindu tradition, practiced widely across all of India, Nepal and Sri Lanka. Modern historians believe that the figure of Shiva as we know him today was built-up over time, with the ideas of many regional sects being amalgamated into a single figure. How the persona of Shiva converged as a composite deity is not well-documented. Axel Michaels explains the composite nature of Shaivism as follows:
Like Vişņu, Śiva is also a high god, who gives his name to a collection of theistic trends and sects: Śaivism. Like Vaişņavism, the term also implies a unity which cannot be clearly found either in religious practice or in philosophical and esoteric doctrine. Furthermore, practice and doctrine must be kept separate.
An example of assimilation took place in Maharashtra, where a regional deity named Khandoba is a patron deity of farming and herding castes. The foremost center of worship of Khandoba in Maharashtra is in Jejuri. Khandoba has been assimilated both as a name for Karttikya and also as a form of Shiva himself in which case he is worshipped in the form of a lingam. Khandoba's varied associations also include an indentification with Surya. The derivation of the name Khandoba has been variously interpreted, and M. S. Mate says that the most commonly-held belief is that it was a distorted form of Skanda, but also notes alternate theories.
The Pashupati Seal
A seal discovered during the excavation of Mohenjo-daro has drawn attention as a possible representation of a "proto-Shiva" figure. This "Pashupati" (Lord of Animals,or Lord of Beings Sanskrit paśupati) seal shows a seated figure, possibly ithyphallic, surrounded by animals. Sir John Marshall and others have claimed that this figure is a prototype of Shiva, and have described the figure as having three faces, seated in a "yoga posture" with the knees out and feet joined. However, this claim is not without its share of critics with some modern academics like Gavin Flood and John Keay characterizing them as unfounded.
Rudra
Shiva as we know him today shares many features with the Vedic god Rudra and both Shiva and Rudra are viewed as the same personality in a number of Hindu traditions. Rudra, the god of the roaring storm, is usually portrayed in accordance with the element he represents as a fierce, destructive deity.
The oldest surviving text of Hinduism is the Rig Veda, which is dated to between 1700-1100 BCE based on linguistic and philological evidence. A god named Rudra is mentioned in the Rig Veda. The name Rudra is still used as a name for Shiva. In RV 2.33 he is described as the "Father of the Maruts", a group of storm gods. Furthermore, the Rudram, one of the most sacred hymns of Hinduism found both in the Rig and the Yajur Vedas, and addressed to Rudra, invokes him as Shiva in several instances.
The identification of Shiva with the older god Rudra is not universally accepted, as Axel Michaels explains:
To what extent Śiva's origins are in fact to be sought in Rudra is extremely unclear. The tendency to consider Śiva an ancient god is based on this identification, even though the facts that justify such a far-reaching assumption are meager.
Rudra is called "The Archer" (Sanskrit: Śarva) and the arrow is an essential attribute of Rudra. This name appears in the Shiva Sahasranama, and R. K. Sharma notes that it is used as a name of Shiva often in later languages. The word is derived from the Sanskrit root śarv- which means "to injure" or "to kill" and Sharma uses that general sense in his interpretive translation of the name Śarva as "One who can kill the forces of darkness". The names Dhanvin ("Bowman") and Bāṇahasta ("Archer", literally "Armed with arrows in his hands") also refer to archery.
Identification with Vedic Deities
Shiva's rise to a major position in the pantheon was facilitated by his identification with a host of Vedic deities, including Agni, Indra, Prajāpati, Vāyu, and others.
Agni
Rudra and Agni have a close relationship. The identification between Agni and Rudra in the Vedic literature was an important factor in the process of Rudra's gradual development into the later character as Rudra-Shiva. The identification of Agni with Rudra is explicitly noted in the Nirukta, an important early text on etymology, which says "Agni is called Rudra also". The interconnections between the two deities are complex, and according to Stella Kramrisch:
The fire myth of Rudra-Śiva plays on the whole gamut of fire, valuing all its potentialities and phases, from conflagration to illumination.
In the Śatarudrīa, some epithets of Rudra such as Sasipañjara ("Of golden red hue as of flame") and Tivaṣīmati ("Flaming bright") suggest a fusing of the two deities. Agni is said to be a bull and Lord Shiva possesses a bull as his vehicle, Nandi. The horns of Agni, who is sometimes characterized as a bull, are mentioned. In medieval sculpture both Agni and the form of Shiva known as Bhairava have flaming hair as a special feature.
Indra
Koenraad Elst proposes that Shiva of Puranic Hinduism is a continuation of the Vedic Indra. He gives several reasons for his hypothesis. Both Shiva and Indra are known for having a thirst for Soma. Both are associated with mountains, rivers, male fertility, fierceness, fearlessness, warfare, transgression of established mores, the Aum sound, the Supreme Self. In the Rig Veda the term śiva is used to refer to Indra.
Indra, like Shiva, is likened to a bull. In the Rig Veda, Rudra is the father of the Maruts, but he is never associated with their warlike exploits as is Indra. In the present form of Hinduism, Indra and Shiva are considered as distinct deities.
Attributes
- Third Eye: Shiva is often depicted with a third eye with which he burned Desire (Kāma) to ashes. There has been controversy regarding the original meaning of Shiva's name Tryambakam, which occurs in many scriptural sources. In classical Sanskrit the word ambaka denotes "an eye", and in the Mahabharata Shiva is depicted as three-eyed, so this name is sometimes translated as "Having Three Eyes". However, in Vedic Sanskrit the word ambā or ambikā means "mother", and this early meaning of the word is the basis for the translation "Having Three Mothers" that was used by Max Müller and Arthur Macdonell. Since no story is known in which Shiva had three mothers, E. Washburn Hopkins suggested that the name refers not to three mothers, but to three Mother-goddesses who are collectively called the Ambikās. Other related translations have been "having three wives or sisters", or based on the idea that the name actually refers to the oblations given to Rudra, which according to some traditions were shared with the goddess Ambikā.
- Blue Throat: The epithet Nīlakaṇtha (nīla = blue, kaṇtha = throat) refers to a story in which Shiva drank the poison churned up from the world ocean.
- Crescent Moon: Shiva bears on his head the crescent of the moon. The epithet Chandraśekhara ("Having the moon as his crest" - chandra = Moon, śekhara = crest, crown) refers to this feature. The placement of the moon on his head as a standard iconographic feature dates to the period when Rudra rose to prominence and became the major deity Rudra-Shiva. The origin of this linkage may be due to the identification of the moon with Soma, and there is a hymn in the Rig Veda where Soma and Rudra are jointly emplored, and in later literature Soma and Rudra came to be identified with one another, as were Soma and the Moon.
- Matted Hair: Shiva's distinctive hair style is noted in the epithets Jaṭin, "The One with matted hair" and Kapardin, "Endowed with matted hair" or "wearing his hair wound in a braid in a shell-like (kaparda) fashion". A kaparda is a cowrie shell, or a braid of hair in the form of a shell, or more generally hair that is shaggy or curly.
- Sacred Ganga: The Ganga river flows from the matted hair of Shiva. The epithet Gaṅgādhara ("Bearer of the river Gaṅgā") refers to this feature. The Ganga (Ganges), one of the major rivers of the country, is said to have made her abode in Shiva's hair.
- Ashes: Shiva smears his body with ashes (bhasma). Some forms of Shiva, such as Bhairava, are associated with a very old Indian tradition of cremation-ground asceticism that was practiced by some groups who were outside the fold of brahmanic orthodoxy. These practices associated with cremation grounds are also mentioned in the Pali canon of Theravada Buddhism. One epithet for Shiva is "Inhabitant of the cremation ground" (Sanskrit: śmaśānavāsin, also spelled Shmashanavasin) referring to this connection.
- Tiger skin: He is often shown seated upon a tiger skin, an honour reserved for the most accomplished of Hindu ascetics, the Brahmarishis.
- Serpents: Shiva is often shown garlanded with a snake.
- Trident: (Trishula): Shiva's particular weapon is the trident.
- Drum: A small drum shaped like an hourglass is known as a damaru. This is one of the attributes of Shiva in his famous dancing representation known as Nataraja. A specific hand gesture (mudra) called ḍamaru-hasta is used to hold the drum. This drum is particularly used as an emblem by members of the Kāpālika sect.
- Nandī: Nandī also known as Nandin, is the name of the bull that serves as Shiva's mount. Shiva's association with cattle is reflected in his name Paśupati or Pashupati, translated by Sharma as "Lord of cattle" and by Kramrisch as "Lord of Animals", who notes that it is particularly used as an epithet of Rudra.
- Gaṇa: are attendants of Shiva and live in Kailash. They are often referred to as the Boothaganas, or ghostly hosts, on account of their nature. Generally benign, except when their Lord is transgressed against, they are often invoked to intercede with the Lord on behalf of the devotee. Ganesha was chosen as their leader by Shiva, hence Ganesha's title gaṇa-īśa or gaṇa-pati, "lord of the gaṇas".
- Mount Kailāsa: Mount Kailash in the Himalayas is his traditional abode. In Hindu mythology, Mount Kailāsa is conceived as resembling a Linga, representing the center of the universe.
- Varanasi: Varanasi (Benares) is considered as the city specially-loved by Shiva, and is one of the holiest places of pilgrimage in India. It is referred to, in religious contexts, as Kashi.
According to Gavin Flood, "Śiva is a god of ambiguity and paradox", whose attributes include opposing themes. The ambivalent nature of this deity is apparent in some of his names and the stories told about him.
Destroyer versus Benefactor
In the Yajurveda two contrary sets of attributes for both malignant or terrific and benign or auspicious forms can be found, leading Chakravarti to conclude that "all the basic elements which created the complex Rudra-Śiva sect of later ages are to be found here." In the Mahabharata, Shiva is depicted as "the standard of invincibility, might, and terror", as well as a figure of honor, delight, and brilliance. The duality of Shiva's fearful and auspicious attributes appears in contrasted names.
The name Rudra reflects his fearsome aspects. According to traditional etymologies, the Sanskrit name Rudra is derived from the root rud- which means "to cry, howl." Stella Kramrisch notes a different etymology connected with the adjectival form raudra, which means wild, of rudra nature, and translates the name Rudra as "the Wild One" or "the Fierce God". R. K. Sharma follows this alternate etymology and translates the name as "Terrible". Hara is an important name that occurs three times in the Anushasanaparvan version of the Shiva sahasranama, where it is translated in different ways each time it occurs, following a commentorial tradition of not repeating an interpretation. Sharma translates the three as "One who captivates", "One who consolidates", and "One who destroys." Kramrisch translates it as "The Ravisher". Another of Shiva's fearsome forms is as Kāla, "Time", and as Mahākāla, "Great Time", which ultimately destroys all things. Bhairava, "Terrible" or "Frightful" is a fierce form associated with annihilation.
In contrast, the name Śaṇkara, "Beneficent" or "Conferring Happiness" reflects his benign form. This name was adopted by the great Vedanta philosopher Śaṇkara (c. 788-820 CE), who is also known as Shankaracharya. The name Śambhu, "Causing Happiness", also reflects this benign aspect.
Ascetic versus Householder
He is depicted as both an ascetic yogin and as a householder, roles which are mutually exclusive in Hindu society. When depicted as a yogin he may be shown sitting and meditating. His epithet Mahāyogin (The Great Yogi: Mahā = great, Yogin = one who practices Yoga) refers to his association with yoga. While Vedic religion was conceived mainly in terms of sacrifice, it was during the Epic period that concepts of tapas, yoga, and asceticism, became more important, and the depiction of Shiva as an ascetic sitting in philosophical isolation reflects these later concepts.
As a family man and householder he has a wife, Parvati (also known as Umā), and two sons, Ganesha and Skanda. His epithet Umāpati ("The husband of Umā") refers to this idea, and Sharma notes that two other variants of this name that mean the same thing, Umākānta and Umādhava, also appear in the sahasranama. Umā in epic literature is known by many names, including Pārvatī. She is identified with Devi, the Divine Mother, and with Shakti (divine energy).
Shiva and Parvati are the parents of Karthikeya and Ganesha. Karthikeya is worshipped in southern India (especially in Tamil Nadu and Karnataka) by the names Subrahmanyan, Shanmughan, Swaminathan and Murugan, and in northern India, is better known by the names Skanda, Kumara, or Karttikeya.
Nataraja
The depiction of Shiva as Nataraja ("Lord of Dance") is popular. The names Nartaka ("Dancer") and Nityanarta ("Eternal Dancer") appear in the Shiva Sahasranama. His association with dance and also with music is prominent in the Puranic period. In addition to the specific iconographic form known as Nataraja, various other types of dancing forms are found in all parts of India, with many well-defined varieties in Tamil Nadu (in southern India) in particular.
Dakṣiṇāmūrti
Dakṣiṇāmūrti literally describes a form (mūrti) of Shiva facing south (dakṣiṇa). This form represents Shiva in his aspect as a teacher of yoga, music, and wisdom, and giving exposition on the shastras. This iconographic form for depicting Shiva in Indian art is mostly from Tamil Nadu. Elements of this motif can include Shiva seated upon a deer-throne and surrounded by sages who are receiving his instruction.
Mruthyunjaya
Literally translated as 'victor over death', this is an aspect of Shiva worshipped as the conqueror of Death as manifested in the Hindu lord of death, Yama. The particular legend in question deals with the sage Markandeya, who was fated to die at the age of sixteen. On account of the sage's worship and devotion to Shiva, the Lord vanquished Yama to liberate his devotee from death. Shiva is often worshipped as Mruthyunjaya by the aged or ill, to ward off death and mitigate its harshness when it does occur. He is worshipped as such at the temples of Thirupainyeeli, near Trichinopoly, and at a shrine in Thirukadaiyur, near Chidambaram.
Ardhanarishvara
An iconographic representation of Shiva called Ardhanarishvara shows him with one half of the body as male, and the other half as female. According to Ellen Goldberg, the traditional Sanskrit name for this form, (Ardhanārīśvara) is best translated as "the lord who is half woman", and not as "half-man, half-woman".
Tripurāntaka
Shiva is often depicted as an archer in the act of destroying the triple fortresses, Tripura, of the Asuras. Shiva's name Tripurāntaka, "Ender of Tripura", refers to this important story.
Lingam
Apart from anthropomorphic images of Shiva, the worship of Shiva in the form of a lingam is also important. These are depicted in various forms. One common form is the shape of a vertical rounded column.
The Five Mantras
Five is a sacred number for Shiva. One of his most important mantras has five syllables (namaḥ śivāya).
Shiva's body is said to consist of five mantras, called the pañcabrahmans: As forms of god, each of these have their own names and distinct iconography:
- Sadyojāta
- Vāmadeva
- Aghora
- Tatpuruṣa
- Īsāna
Through these transcendent categories, Śiva, the ultimate reality, becomes the efficient and material cause of all that exists.
According to the Pañcabrahma Upanishad:
One should know all things of the phenomenal world as of a fivefold character, for the reason that the eternal verity of Śiva is of the character of the fivefold Brahman.

A statue in Bangalore depicting Shiva meditating

An Indus Valley seal with the seated figure termed pashupati.

Three-headed Shiva, Gandhara, 2nd century

Shiva with Parvati. Shiva is depicted three-eyed, with crescent moon on his head, the Ganga flowing through his matted hair, wearing ornaments of serpents and a skull necklace, covered in ashes and Trisula and Damaru are seen in the background.

Shiva Bearing the Descent of the Ganges River as Parvati and Bhagiratha, and the bull Nandi look, folio from a Hindi manuscript by the saint Narayan, circa 1740

Shiva carrying the corpse of his first consort Dakshayani

An illustration of the family of Shiva, consisting of Shiva, Parvati, Ganesha and Skanda

Bronze Chola Statue depicting Shiva dancing as Nataraja. Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City.

Chola bronze from the 11th century. Shiva in the form of Ardhanarisvara.

Adoration of Five-headed Shiva by Vishnu (blue figure, to left of Shiva),Brahma (four headed figure to the right of Shiva), Ganesha (elephant-headed son of Shiva, bottom left) and other deities.

Vishnu (left half - blue) and Shiva (right half - white)

108 shiva lingas carved on the rock at the banks of river Tungabhadra, Hampi

A statue of Shiva near Indira Gandhi International Airport, Delhi